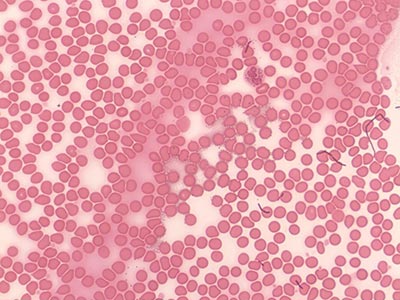
Bacteria, Yeast, and Blood
(1000X total magnification)
This mixed smear shows typical bacilli, yeast, and human blood cells. Pay particular attention to their respective sizes. Even the biggest bacteria are smaller than yeast, which are still smaller than a typical human red blood cell.
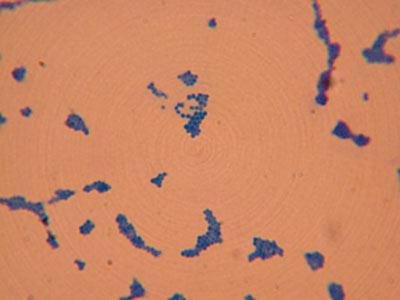
Staphylococcus aureus
(1000X total magnification)
- Domain: Bacteria
- Kingdom: Eubacteria
- Phylum: Firmicutes
- Class: Coccus
- Order: Bacillales
- Family: Staphylococcaceae
- Genus: Staphylococcus
- Species: S. aureus
Gram-positive coccal bacterium that is a member of the Firmicutes, and is frequently found in the human respiratory tract and on the skin.
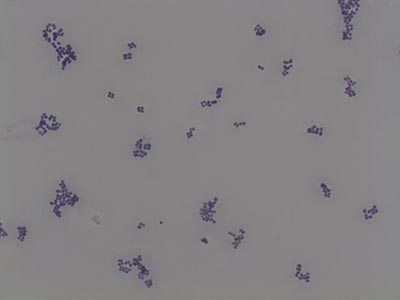
Micrococcus luteus
(1000X total magnification)
These Gram positive cocci, typically arranged in tetrads, are normal flora of mammalian skin.
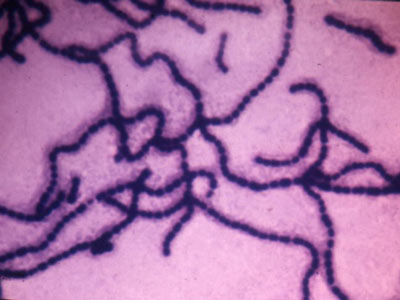
Streptococcus faecalis
(1000X total magnification)
Shows typical chains of cocci.
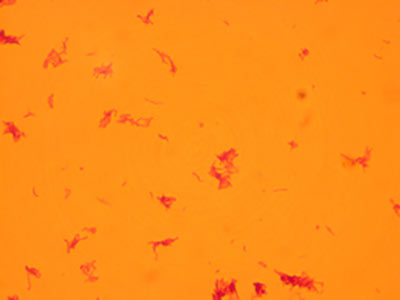
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
(1000X total magnification)
These Gram-resistant, slightly curved bacilli are the causative agents of tuberculosis. Due to a special wax in their cell membrane, these organisms do not readily take up dye from a typical gram stain. Instead, an acid-fast stain using either heat or detergent is performed in order to break through this protective waxy layer.
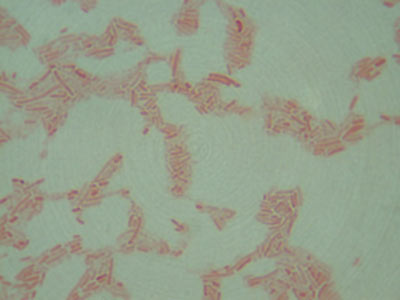
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
(1000X total magnification)
These Gram negative, slightly curved bacilli cause infections in wounds, burns, and urinary tracts.
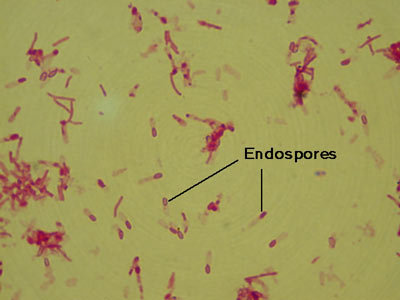
Clostridium tetani
(1000X total magnification)
Observe the characteristic drumstick shape of these cells. The endospores are rounded and terminal. These anaerobes are the causative agent of tetanus.
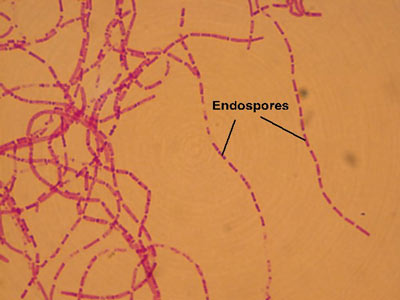
Bacillus anthracis
(1000X total magnification)
These long chains of rod-shaped cells have centrally located endospores. Endospores are a resting structure formed inside the cell that allows the bacteria to survive harsh conditions for extended periods. Look for red spores inside blue rods.
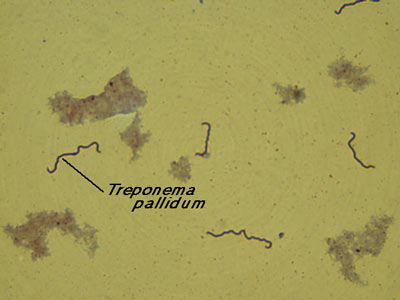
Treponema pallidum
(1000X total magnification)
Treponema pallidum is the causative agent of syphilis. It is a spirochete that is best viewed live with dark-field microscopy.
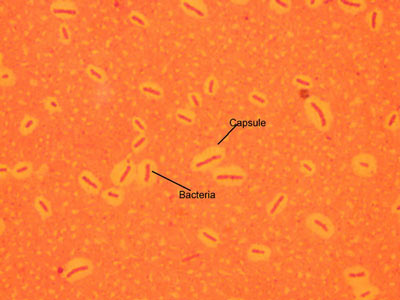
Bacterial Capsules
(1000X total magnification)
Notice the background of the slide is colored so that you can see the protective slime coating secreted by many bacteria.
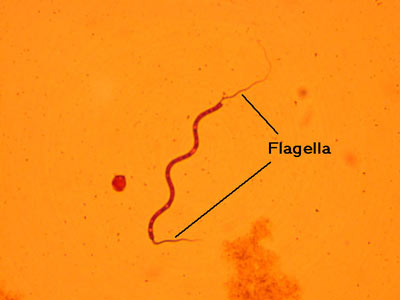
Bacterial Flagella – Peritrichous
(1000X total magnification)
Proteus vulgaris, a bacillus, moves by peritrichous flagella; notice flagella distributed all around the bacterial cell.
Many bacteria are motile because they possess whip-like flagella. Peritrichous flagella are distributed all over the cell; monotrichous flagella indicate just one; tufts of flagella at both ends of the cell are amphitrichous; and tufts of flagella at one end of the cell are lophotrichous.
This is a very difficult and time-consuming stain because the flagella are very thin and fragile.
Bacterial Flagella – Polar amphitrichous
(1000X total magnification)
Spirillum volutans, a helical cell, moves by polar amphitrichous flagella; notice flagella at each end of the bacterial cell.
Many bacteria are motile because they possess whip-like flagella. Peritrichous flagella are distributed all over the cell; monotrichous flagella indicate just one; tufts of flagella at both ends of the cell are amphitrichous; and tufts of flagella at one end of the cell are lophotrichous.
This is a very difficult and time-consuming stain because the flagella are very thin and fragile.






